Published by Beata Boczkowska, Ph.D. on May 25, 2023 12:43:35 PM
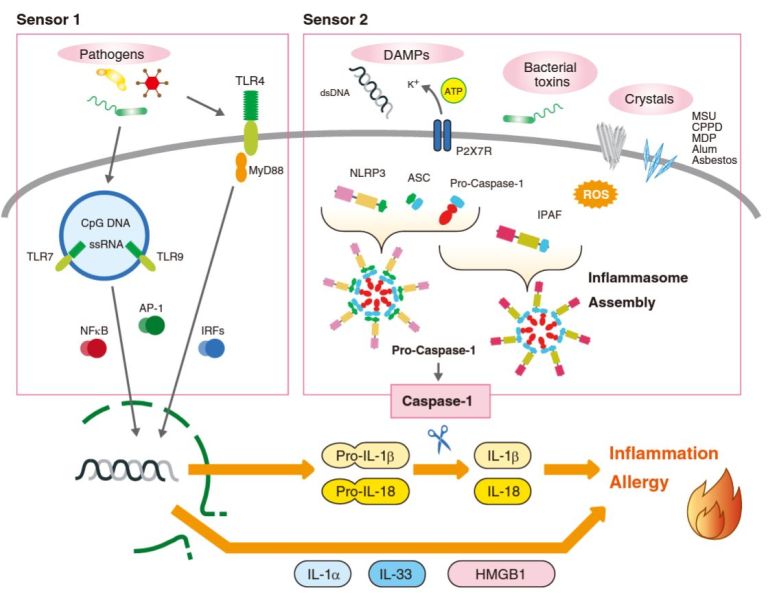
Interleukin-18 (IL-18) is an effective pro-inflammatory cytokine for the host defense against infections and controls the innate and acquired immune response. Both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells, including monocytes, macrophages, keratinocytes, and mesenchymal cells produce IL-18. IL-18 can increase Th1 responses and is critical for IFN-gamma production. IL-18 is regulated by IL-18BP by inhibiting the biological activity of IL-18, thereby reducing IFN-gamma production in turn suppressing the Th1 immune responses. The dysregulation of the IL-18/IL-18BP balance is associated with multiple biological effects and pathological outcomes (1). Both IL-18 and IL18BP are connected to developing psoriasis, atopic dermatitis (AD), lupus erythematosus (LE), and other inflammatory skin diseases. Still, IL-18 is more prominently involved with chronic inflammation and autoimmune disease such as inflammatory bowel diseases, type I diabetes mellitus, chronic liver disease, adult-onset Still’s disease, hemophagocytic syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Due to the biological properties of IL-18 and its pathological role in different diseases, it is not surprising that drug discovery and therapies are focused on IL-18 and the control of its more pathological outcomes. Using monoclonal antibodies, IL-18 is prevented by inhibiting its production in cells and its secretion from cells. However, most monoclonal antibody therapies that target IL-18 alone had only partial effectiveness or complete ineffectiveness in vitro, in vivo, and human studies (2). The unsuccessfulness of these monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-18 alone may be more due to the contribution of the intrinsic involvement of other cytokines and proteins in the signaling pathway of many inflammatory diseases. Currently, drug therapy is becoming more focused on IL-18 inhibitors or agonists in addition to other cytokines. The table summarizes some of the IL-18 inhibitors and IL-18BP drugs in clinical trials and preclinical studies for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
|
Drug Category |
Application |
Mechanism |
Clinical Phase Status |
|
Recombinant human IL-18 binding protein |
Macrophage Activation Syndrome/Immune System Diseases/Adult-Onset Still’s Disease |
IL-18 inhibitor |
Phase III |
|
Biological products |
Atopic Dermatitis/Pulmonary Sarcoidosis |
IL-18 inhibitor |
Phase II |
|
Monoclonal antibody |
Adult-Onset Still’s Disease/Autoimmune Diseases |
IL-18 inhibitor |
Phase I |
|
Biological products |
Melanoma/Carcinoma/Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
IL-18 agonist |
Phase II |
|
Fusion protein |
Adult-Onset Still’s Disease/Rheumatoid Arthritis/Inflammatory Bowel Diseases |
IL-18 inhibitor |
Drug discovery |
|
Recombinant human IL-18 binding protein |
Psoriasis/Rheumatoid Arthritis/Crohn Disease/Autoimmune Diseases |
IL-18 inhibitor |
Phase II (Terminated) |
|
Fusion protein |
Psoriasis/Myocardial Ischemia/Neoplasm Metastasis |
IL-18 Inhibitor, IL-1R1 antagonist |
Preclinical (Progression free) |
IL-18 performs a critical role in the pathogenesis of some inflammatory diseases. IL-18 inhibitors and IL-18BP agonists are promising candidates for therapy of diverse medical conditions, including acute and chronic inflammation. Clinical studies are indicating the prominent role of IL-18 in Psoriasis, MG, and other diseases. Nonetheless, additional research and clinical trials of IL-18 BP and other antibodies are necessary to properly ascertain the role of IL-18 in treating inflammatory diseases. Hence, research will continue into IL-BP and other drugs affecting IL-18 for the treatment and control of pathogenic inflammatory conditions.
MBL International offers a wide variety of products to help in your research of IL-18.
References
- Harel, Mathilde, et al. "Balance between interleukin-18 and interleukin-18 binding protein in auto-inflammatory diseases." Cytokine 150 (2022): 155781.
- Ihim, Stella Amarachi, et al. "Interleukin-18 cytokine in immunity, inflammation, and autoimmunity: Biological role in induction, regulation, and treatment." Frontiers in Immunology (2022): 4470.
